Indian Railway Zones
Indian Railways is a department owned and controlled by the Government of India, via the Ministry of Railways. Indian Railways is administered by the ✅ Railway Board, which has a financial commissioner, five members and a chairman. Indian Railway Zones are following.
- Indian Railway History
Railway zones
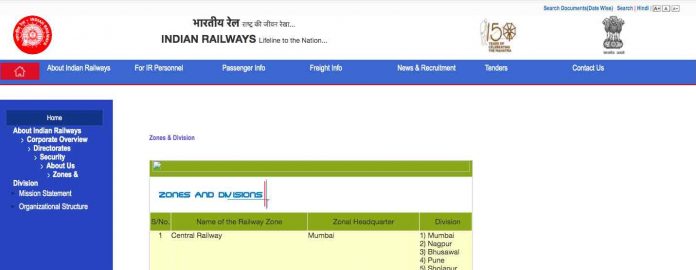
Indian Railways is divided into zones, which are further sub-divided into divisions. The number of zones in Indian Railways increased from six to eight in 1951, nine in 1952, and finally ✅ 16 in 2003. Each zonal railway is made up of a certain number of divisions, each having a divisional headquarters. There are a total of sixty-seven divisions. The Kolkata Metro is owned and operated by Indian Railways, but is not a part of any of the zones. It is administratively considered to have the status of a zonal railway.
Each of the sixteen zones, as well as the ✅ Kolkata Metro, is headed by a General Manager (GM) who reports directly to the Railway Board. The zones are further divided into divisions under the control of Divisional Railway Managers (DRM). The divisional officers of engineering, mechanical, electrical, signal and telecommunication, accounts, personnel, operating, commercial and safety branches report to the respective Divisional Manager and are in charge of operation and maintenance of assets. Further down the hierarchy tree are the Station Masters who control individual stations and the train movement through the track territory under their stations’ administration.
- Latest Station Name And Station Code List
- Southern Railway History
Indian Railway zones List
| Sl. No | Name | Abbr. | Date Established | Headquarters | Divisions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Central Railway | CR | November 5, 1951 | Mumbai | Mumbai, Bhusawal, Pune, Solapur, Nagpur |
| 2. | East Central Railway | ECR | October 1, 2002 | Hajipur | Danapur, Dhanbad, Mughalsarai, Samastipur, Sonpur |
| 3. | East Coast Railway | ECoR | April 1, 2003 | Bhubaneswar | Khurda Road, Sambalpur, Visakhapatnam |
| 4. | Eastern Railway | ER | April, 1952 | Kolkata | Howrah, Sealdah, Asansol, Malda |
| 5. | North Central Railway | NCR | April 1, 2003 | Allahabad | Allahabad, Agra, Jhansi |
| 6. | North Eastern Railway | NER | 1952 | Gorakhpur | Izzatnagar, Lucknow, Varanasi |
| 7. | North Western Railway | NWR | October 1, 2002 | Jaipur | Jaipur, Ajmer, Bikaner, Jodhpur |
| 8. | Northeast Frontier Railway | NFR | 1958 | Guwahati | Alipurduar, Katihar, Lumding, Rangia, Tinsukia |
| 9. | Northern Railway | NR | April 14, 1952 | Delhi | Delhi, Ambala, Firozpur, Lucknow, Moradabad |
| 10. | South Central Railway | SCR | October 2, 1966 | Secunderabad | Secunderabad, Hyderabad, Guntakal, Guntur, Nanded, Vijayawada |
| 11. | South East Central Railway | SECR | April 1, 2003 | Bilaspur, CG | Bilaspur, Raipur, Nagpur |
| 12. | South Eastern Railway | SER | 1955 | Kolkata | Adra, Chakradharpur, Kharagpur, Ranchi |
| 13. | South Western Railway | SWR | April 1, 2003 | Hubli | Hubli, Bangalore, Mysore |
| 14. | Southern Railway | SR | April 14, 1951 | Chennai | Chennai, Madurai, Palakkad, Salem, Tiruchchirapalli, Thiruvanathapuram |
| 15. | West Central Railway | WCR | April 1, 2003 | Jabalpur | Jabalpur, Bhopal, Kota |
| 16. | Western Railway | WR | November 5, 1951 | Mumbai | Mumbai Central, Vadodara, Ratlam, Ahmedabad, Rajkot, Bhavnagar |